Accounts Finalization: Step-by-Step Guide with 1-Page Revision Chart
Introduction
Accounts Finalization is one of the most important concepts in accounting, especially for commerce students, CA/CS/CMA aspirants, and practical accountants.
Many learners understand journal entries and ledger posting but get confused when it comes to closing the books and preparing final accounts.
This blog explains Accounts Finalization in a simple, step-by-step manner, supported by a 1-page revision chart that helps in quick recall before exams or practical work.
What is Accounts Finalization?
Accounts Finalization is the process of closing the books of accounts at the end of an accounting period by making necessary adjustments and preparing the final financial statements.
One-line definition (Exam Ready):
Accounts finalization is the process of closing books of accounts after adjustments and preparing final accounts to determine profit or loss and financial position.
Objectives of Accounts Finalization
Accounts Finalization is carried out to:
- Ascertain Gross Profit and Net Profit
- Determine the financial position of the business
- Ensure a true and fair view of accounts
- Comply with Income Tax, GST, and audit requirements
- Support management decision-making
Step-by-Step Process of Accounts Finalization
Step 1: Collection of Accounting Data
All financial documents of the period are collected, such as:
- Sales and purchase invoices
- Expense bills and vouchers
- Bank statements
- Cash book
- Fixed asset and loan details
👉 Purpose: To ensure no transaction is missed.
Step 2: Recording of Transactions
- Journal entries are passed
- Entries are posted into ledger accounts
- Cash book and bank book are updated
👉 Purpose: To properly record business transactions.
Step 3: Preparation of Trial Balance
- Ledger balances are extracted
- Debit total is matched with credit total
👉 Purpose: To check arithmetical accuracy of books.
Step 4: Verification of Trial Balance
- Identify unusual balances
- Compare figures with previous year
- Detect missing or incorrect entries
👉 Purpose: To detect errors and inconsistencies.
Step 5: Passing Adjusting Entries (Core Step)
This is the heart of accounts finalization.
Common adjustments include:
- Outstanding expenses
- Prepaid expenses
- Accrued income
- Income received in advance
- Depreciation
- Closing stock
- Provisions and reserves
👉 Purpose: To follow the accrual and matching principles.
Step 6: Preparation of Final Accounts
1. Trading Account
Prepared to calculate Gross Profit or Gross Loss.
Includes:
- Opening stock
- Purchases and direct expenses
- Sales
- Closing stock
2. Profit & Loss Account
Prepared to calculate Net Profit or Net Loss.
Includes:
- Gross profit
- Indirect expenses
- Other incomes
3. Balance Sheet
Prepared to show the financial position on a particular date.
Includes:
- Assets (Fixed & Current)
- Liabilities (Capital, Loans, Creditors)
Step 7: Review and Compliance Check
- Tax compliance (Income Tax, GST, TDS/TCS)
- Audit applicability
- Management approval
👉 Purpose: To avoid future notices and penalties.
Step 8: Closing Entries and Carry Forward
- Income and expense accounts are closed
- Balances are carried forward to next year
👉 Purpose: To start the new accounting year cleanly.
Important Adjustments to Remember (High Exam Weightage)
- Outstanding expenses
- Prepaid expenses
- Accrued income
- Income received in advance
- Depreciation
- Closing stock
- Provisions & reserves
📌 These adjustments ensure the true profit and correct balance sheet.
Accounting Concepts Used in Accounts Finalization
- Accrual Concept
- Matching Concept
- Prudence
- Consistency
- Going Concern
These concepts ensure accuracy and reliability of financial statements.
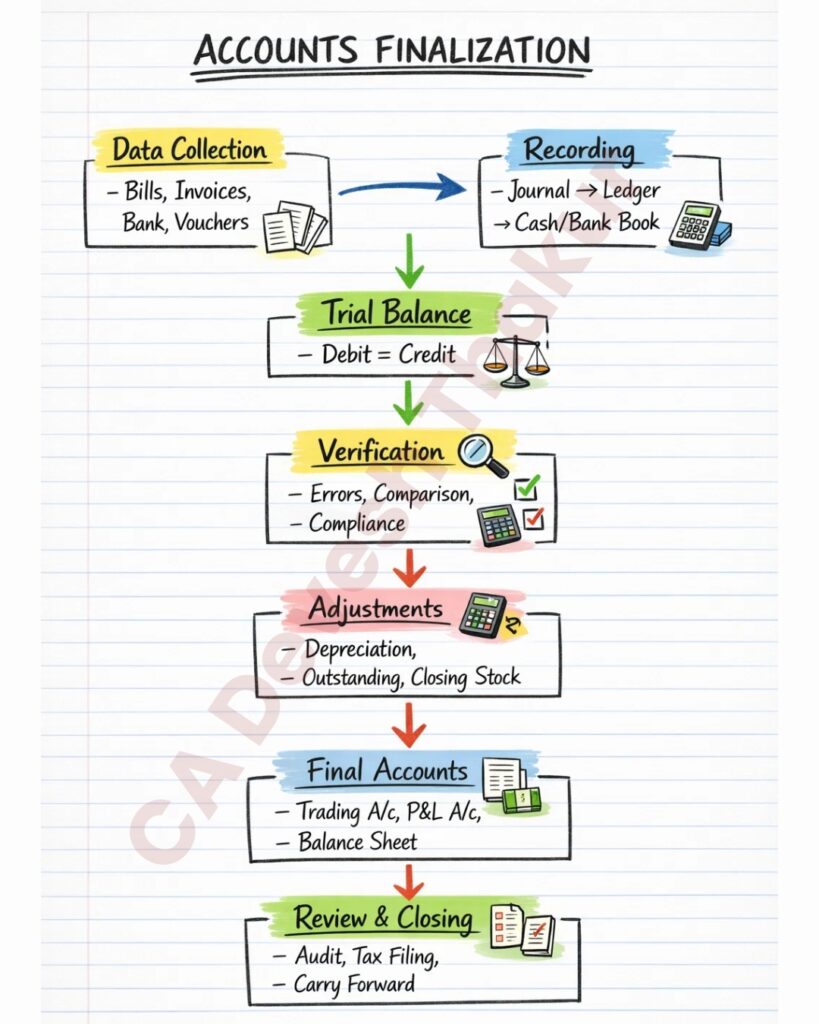
1-Page Revision Chart – Memory Trick 🧠
CRCVAFRC
Collect → Record → Check → Verify → Adjust → Final Accounts → Review → Close
| STEP | PARTICULARS | KEY POINTS |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | Data Collection | Bills, invoices, bank statements, vouchers |
| 2️⃣ | Recording | Journal entries → Ledger posting |
| 3️⃣ | Trial Balance | Debit = Credit check |
| 4️⃣ | Verification | Errors, missing entries, unusual balances |
| 5️⃣ | Adjustments | Outstanding, prepaid, depreciation, stock |
| 6️⃣ | Final Accounts | Trading A/c, P&L A/c, Balance Sheet |
| 7️⃣ | Review | Compliance, audit, approvals |
| 8️⃣ | Closing | Closing entries & carry forward |
This flow helps students revise the entire topic in minutes.
Why Accounts Finalization is Important for Students & Professionals
- Frequently asked in CA Foundation, Class 11 & 12 exams
- Forms the base for tax computation
- Essential for business analysis and reporting
- Required for audits, loans, and compliance
Conclusion
Accounts Finalization is not just an exam topic—it is a practical accounting skill.
Once the step-by-step process and adjustments logic are clear, the topic becomes easy and scoring.
If you master this roadmap, you can confidently handle:
✔ Exams
✔ Office work
✔ Practical accounting cases




