Introduction
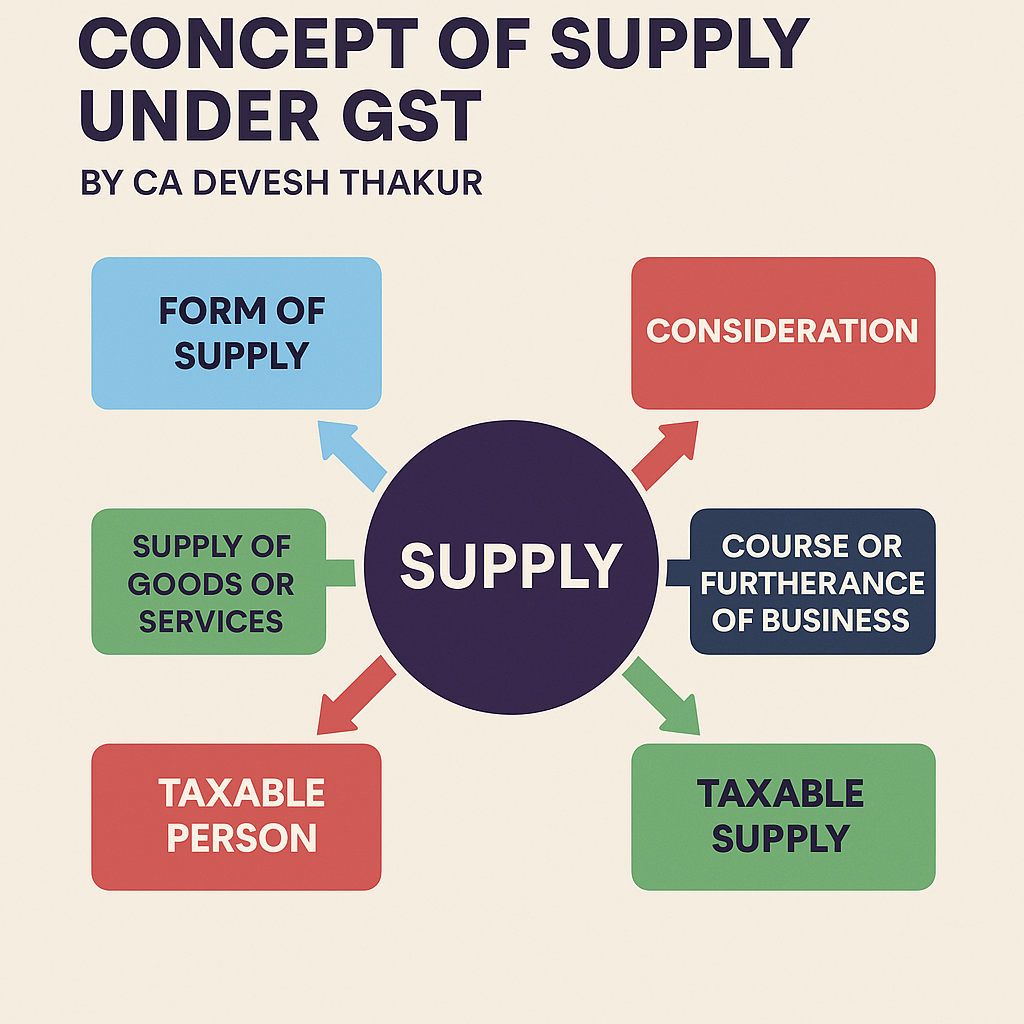
The taxable event under GST is the “Supply” of goods or services or both. This marks a major shift from the earlier indirect tax regime where events like sale, manufacture, or provision of service triggered taxation. Under GST, the concept of supply is broad, inclusive, and well-defined in Section 7 of the CGST Act, 2017.
Let’s break it down in simple terms using legal references, practical examples, and visual concepts.
Legal Reference: Section 7 of CGST Act, 2017
Section 7 defines supply and includes:
- All forms of supply for consideration in the course or furtherance of business
- Import of services for consideration (even if not for business)
- Certain activities specified in Schedule I even if made without consideration
Effective from 01.07.2017 via Notification No. 09/2017-CT dated 28.06.2017
What is Included in “Supply”?
🔹 1. Normal Supply – Section 7(1)(a)
Includes:
- Sale, Transfer, Barter, Exchange
- License, Lease, Rental, Disposal
Conditions:
- For consideration
- By a person
- In the course or furtherance of business
Example:
- Sale of mobile phones to customers
- Renting office space
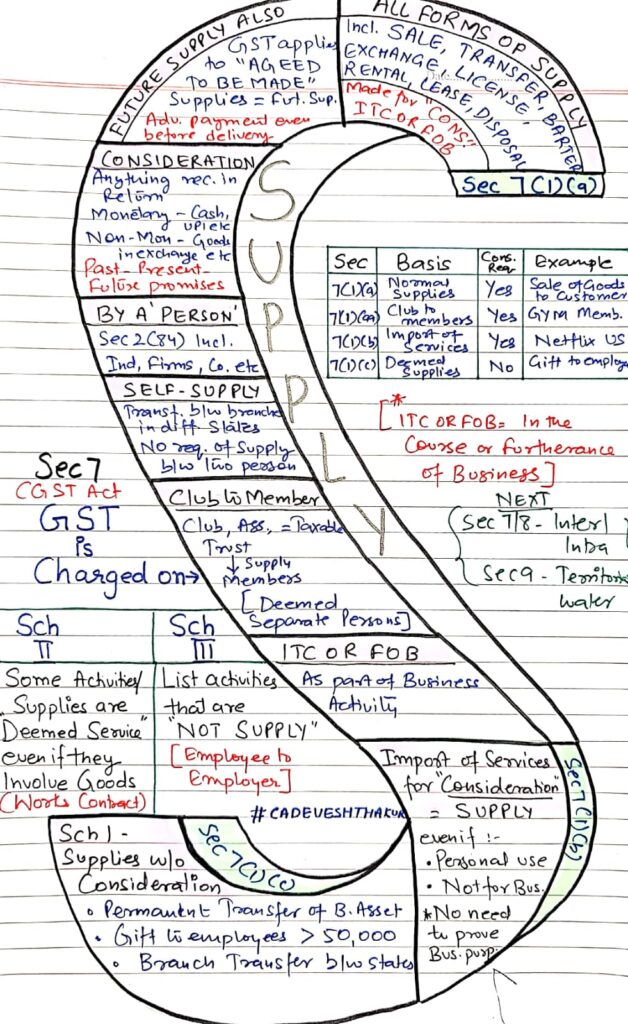
🔹 2. Future Supplies Also Covered
GST applies to agreed-to-be-made supplies too.
Advance received for a future supply = Taxable
Example:
Advance ₹10,000 for service to be delivered next month → GST payable on receipt.
🔹 3. Consideration Must Be Present (Sec 2(31))
Can be:
- Monetary: Cash, UPI, Card
- Non-monetary: Exchange of goods/services
- Past, Present, or Future promises
Example:
- Barter of laptops for printers
- Promise to deliver goods in exchange for services
🔹 4. Supply by a Person – Section 2(84)
“Person” includes:
- Individual
- HUF
- Company
- Partnership
- Trusts, Govt. bodies, etc.
Example:
Supply made by a registered LLP to another business unit
🔹 5. Self-Supply is Taxable
Distinct persons under GST = Separate GSTINs
Transfer between branches in different states = Supply
Example:
Stock transferred from Delhi Head Office to Bangalore branch → GST applicable
🔹 6. Club/Association to Members – Section 7(1)(aa)
Inserted via Finance Act, 2021 (retrospective effect from 01.07.2017)
- Supplies by clubs, associations, trusts to members are taxable
- Mutuality principle doesn’t apply
Example:
Gym membership fees collected by an association → Supply
🔹 7. Import of Services – Section 7(1)(b)
- Import for consideration is supply
- Even if used for personal or non-business purpose
Example:
Netflix US subscription for personal entertainment = Supply
🔹 8. Deemed Supply Without Consideration – Section 7(1)(c)
As per Schedule I, following are deemed as supply even without consideration:
Examples:
- Permanent transfer of business assets
- Gift > ₹50,000 to employees
- Supply between related/distinct persons (e.g., inter-state branch transfer)
Classification Based on Schedule
| Schedule | Nature | Example |
| Schedule I | Supply without consideration | Branch transfer, Gift to employee > ₹50,000 |
| Schedule II | Deemed service even if goods used | Renting immovable property, Works contract |
| Schedule III | Not a supply | Employee service to employer, Sale of land/building |
Intra-State vs Inter-State Supply
| Supply Type | Law Applicable | Tax Components |
| Intra-State | CGST + SGST Acts | CGST + SGST |
| Inter-State | IGST Act | IGST |
| Territorial | Sec 9, IGST Act | IGST on marine/water-based |
Reference:
- Sec 7 & 8, IGST Act for classification
- Sec 9, IGST Act for territorial supplies
Section-Wise Summary Table
| Section | Type of Supply | Consideration Needed | Example |
| 7(1)(a) | Normal supply | ✅ Yes | Sale of goods |
| 7(1)(aa) | Club/Association to member | ✅ Yes | GYM membership |
| 7(1)(b) | Import of services | ✅ Yes | Netflix subscription |
| 7(1)(c) | Deemed supplies (Sch I) | ❌ No | Gift > ₹50,000 to employee |
Key Takeaways
- GST is a destination-based consumption tax.
- Supply is the triggering event under GST.
- Future supplies, self-supplies, and imports for personal use are all covered.
- Some activities are taxable even without consideration (Schedule I).
- Others are not treated as supply at all (Schedule III).
FAQs
Q. Is barter considered supply?
Yes, barter is included under Section 7(1)(a).
Q. Are gifts taxable?
Yes, if gifts > ₹50,000 are given by employer to employee (Schedule I).
Q. Are inter-branch transfers taxable?
Yes, if branches are in different states.
Author: CA Devesh Thakur
Category: GST Basics | 30 Days GST Challenge – Day 3
Learn More
Day 2: GST Explained with Simplicity | Threshold, Supply, Types, Valuation & Key Terms