India’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a comprehensive indirect tax reform aimed at unifying multiple taxes into one. Whether you’re a student, small business owner, or finance professional, this detailed explanation will help you understand GST from scratch — with examples, sections, rules, and simplified illustrations.
📍 What Triggers GST? – The Taxable Event
Taxable event under GST is “Supply” of goods or services.
Section 7 of CGST Act defines what is considered supply.
🔹 Types of Supply as per Schedules:
- Schedule I: Treated as supply even without consideration (e.g. free gifts to relatives).
- Schedule II: Deems certain activities as supply of goods/services (e.g. renting immovable property).
- Schedule III: Lists activities not treated as supply (e.g. employee services to employer).
Example:
If a company gifts goods worth ₹20,000 to its branch in another state, it is a taxable supply under Schedule I.
Threshold Limit for GST Registration
Section 22 of CGST Act governs registration thresholds:
| Type of Supply | Normal States | Special Category States |
| Goods | ₹40 lakhs | ₹20 lakhs |
| Services | ₹20 lakhs | ₹10 lakhs |
Example:
A textile trader in Maharashtra must register under GST when their turnover exceeds ₹40 lakhs.
Types of Supply: Intra-State vs Inter-State
🔹 Intra-State Supply
- Supply within the same State or Union Territory.
- Taxes levied: CGST + SGST/UTGST
- Section 8(1) of IGST Act
Example:
Seller (Delhi) → Buyer (Delhi)
→ CGST + SGST apply.
🔹 Inter-State Supply
- Supply between different States.
- Taxes levied: IGST
- Section 7(1) of IGST Act
Example:
Seller (Delhi) → Buyer (Haryana)
→ IGST applies.
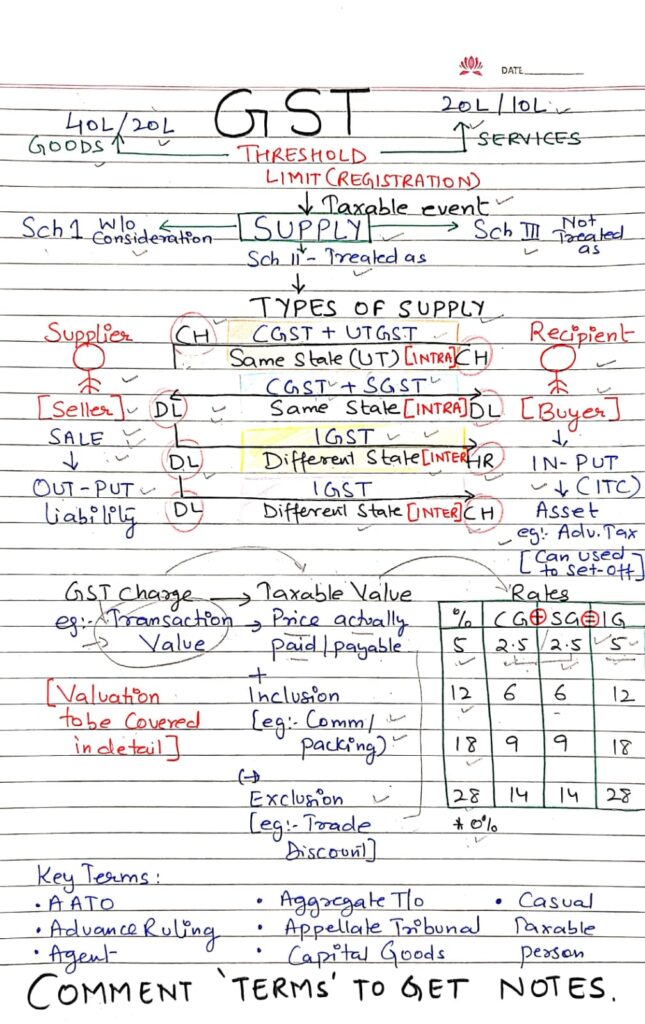
Output Tax Liability vs Input Tax Credit (ITC)
- Section 9: Liability to pay tax on outward supplies.
- Section 16: Entitlement to claim ITC.
Example:
Your outward tax liability = ₹15,000
ITC from purchases = ₹9,000
You pay only the difference = ₹6,000
Valuation Under GST (Section 15)
GST is charged on Transaction Value:
“The price actually paid or payable for the supply of goods or services between unrelated parties.”
✅ Includes:
- Packing charges
- Commissions
- Subsidies (other than govt.)
❌ Excludes:
- Post-supply discounts
- Trade discounts (shown in invoice)
Example:
Price = ₹10,000
- Packing = ₹200
- Commission = ₹300
→ Taxable Value = ₹10,500
📊 GST Rate Structure
| GST Rate | CGST | SGST | IGST |
| 5% | 2.5% | 2.5% | 5% |
| 12% | 6% | 6% | 12% |
| 18% | 9% | 9% | 18% |
| 28% | 14% | 14% | 28% |
| 0% (Exempted) | 0% | 0% | 0% |
Example:
If your goods fall under the 12% slab → You charge CGST @ 6% and SGST @ 6%.
🔑 Important GST Terms You Should Know
✅ AATO (Annual Aggregate Turnover)
Turnover across all states (under same PAN) including exports, exempt & taxable supplies.
👉 Used to determine registration, QRMP scheme eligibility etc.
✅ Advance Ruling
(Section 95–106) – Seek clarity on tax liability before a transaction.
Useful for exporters, startups, and uncertain cases.
✅ Agent
(Section 2(5)) – A person supplying or receiving goods on behalf of someone else.
✅ Appellate Tribunal
(Section 109) – Hears appeals against Appellate Authority decisions.
✅ Capital Goods
(Section 2(19)) – Goods used in the business and capitalized (e.g. machinery). ITC available over time.
✅ Casual Taxable Person
(Section 2(20)) – Someone who occasionally undertakes taxable supply without a fixed business place in that state.
👉 Must take temporary registration.
📌 Conclusion
Understanding GST basics like threshold, supply types, valuation, and key terms sets the foundation for deeper GST mastery. Whether you’re preparing for exams, working in business compliance, or running your own venture — grasping these core concepts is essential.
Stay Tuned for More!
This article is part of our “30 Days GST Challenge” — Day 2: Threshold & Types of Supply
🔗 Read More: