Author: CA Devesh Thakur
Category: GST Basics | 30 Days GST Challenge – Day 6
The concept of Place of Supply (POS) is central to the GST framework, especially in determining the nature of the supply (intra-state or inter-state) and the correct levy of IGST, CGST, or SGST. For services, POS is governed by Sections 12 and 13 of the IGST Act, 2017.
Full Video
This blog focuses on Section 12, which applies when both the supplier and recipient are located in India. In this article, we’ll cover all subsections of Section 12 along with practical examples, simplified interpretations, and relevant legal precedents.
Applicability of Section 12 – Domestic Services
Section 12(1) clarifies that this section applies only where both the supplier and the recipient of the service are located in India. If either party is located outside India, Section 13 becomes applicable.
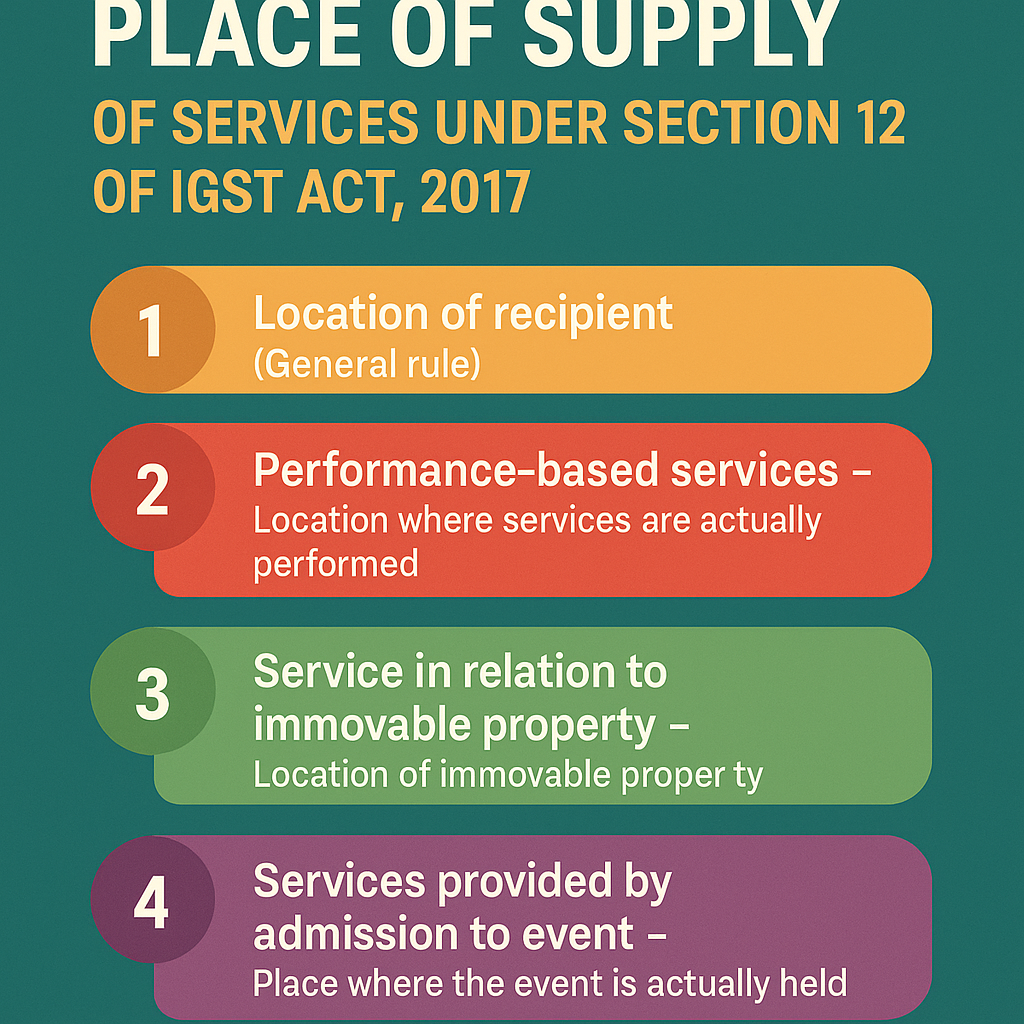
Comprehensive Table: Place of Supply of Services under Section 12 of the IGST Act, 2017
| Section | Category of Service | POS Rule | Example |
| 12(2) | General Rule (when not covered under 3 to 14) | Registered recipient → Location of recipientUnregistered recipient → Address on record, else supplier’s location | CA in Delhi providing consultancy to registered firm in Mumbai |
| 12(3) | Immovable Property/Boat/Vessel services | Location of property, boat, or vesselIf located outside India → POS is location of recipient | Architect designing a property in Goa |
| 12(4) | Performance-based services (Restaurant, Grooming, etc.) | Location where service is actually performed | Haircut in Lucknow |
| 12(5) | Training/Performance Appraisal | Registered → Location of recipientUnregistered → Place where service is performed | Online training for company in Delhi vs. classroom session in Kolkata |
| 12(6) | Admission to Event & Ancillary Services | Place where event is held or park is located | Music show in Mumbai – POS is Mumbai |
| 12(7) | Organisation of Event or Sponsorship | Registered → Location of recipientUnregistered → India – Event location, Outside India – recipient’s location | Conference organised in Bengaluru for unregistered client |
| 12(8) | Transportation of Goods | Registered → Location of recipientUnregistered → Place where goods are handed overFrom 01.10.2023: Rule reset to original position as of 01.07.2017 | Courier from Delhi to US |
| 12(9) | Passenger Transportation | Registered → Location of recipientUnregistered → Embarkation point | Train journey booked by registered office in Mumbai |
| 12(10) | Services on board a conveyance | First scheduled departure point of conveyance | Food sold on flight from Delhi to Mumbai – POS is Delhi |
| 12(13) | Insurance Services | Registered → Location of recipientUnregistered → Location on record | Health insurance sold to individual with address in Jaipur |
| 12(14) | Advertisement to Govt./Statutory Bodies | POS distributed among States/UTs as per agreementElse, Rule 3 of IGST Rules applies | Govt ad campaign aired across 5 states – POS apportioned accordingly |
Multi-State Situations – Proportional Allocation Rules
When services are supplied in relation to immovable property or events spread across multiple States/UTs, the POS is split as follows:
In case of Agreement or Contract:
POS is allocated to each State/UT in proportion to value of services collected or determined under the contract.
In absence of Contract (w.e.f. 01.01.2019):
Rule 4 of IGST Rules, 2017 provides the following basis:
| Service Type | POS Allocation |
| Lodging in hotels/inns/guest houses in contiguous States | Based on nights stayed |
| Marriage/receptions/business events across States | Based on area covered in each State |
| Houseboat or vessel services | Based on time spent in each State (self-declared) |
Judicial Pronouncements Interpreting Place of Supply
1. Ernst & Young Ltd. vs. Addl. Commissioner (2023)
The Delhi High Court clarified that services directly rendered (not arranged or facilitated) do not fall under “intermediary” services. Hence, services rendered by EY to overseas entities qualified as export of services.
2. OHMI Industries Asia Pvt. Ltd. vs. Assistant Commissioner (2023)
The court held that Market Research Services rendered directly to OHMI Japan were not intermediary services. Since the petitioner did not arrange or facilitate the supply from another party, the services qualified as export.
Key Takeaway: Only facilitators are considered intermediaries under Section 2(13). Direct service providers fall outside its scope.
Summary: Core Principles of Section 12
- Location-based logic governs most place of supply rules.
- Recipient’s registration status is crucial in several provisions.
- Event location or service performance location matters in personal or entertainment services.
- Special rules apply for multiple States/UTs, and are based on contracts or prescribed norms.
- Judicial clarity is strengthening the interpretation, especially regarding intermediary services and export classification.
Conclusion
Understanding the correct Place of Supply of Services is essential to ensuring accurate GST compliance. Section 12 offers a detailed framework for various scenarios in the domestic context. Taxpayers, consultants, and businesses must pay close attention to whether the recipient is registered, where the service is performed, and how the value is to be apportioned in multi-state transactions.
For professionals and CA firms, staying updated with the latest rules and judgments is vital to avoid litigation and benefit from GST provisions such as export refunds and correct input tax credit (ITC) allocations.