Welcome to Day 4 of the 30 Days GST Challenge! Today, we focus on one of the foundational aspects of GST — levy and collection of tax and the composition levy mechanism. These elements form the core of how GST functions and applies to various types of supplies and businesses.
What Does “Levy” Mean?
The term “Levy” in a taxation context refers to the imposition or collection of tax by the government. Every tax law has a charging section, which enables the government to impose the tax. Under the GST regime, the levy is governed by:
- Section 9 of CGST/SGST Act – Intra-State supplies
- Section 5 of IGST Act – Inter-State supplies
These sections are considered the charging sections for GST and dictate how tax is levied, collected, and paid.
Levy and Collection of GST (Section 9 of CGST Act & Section 5 of IGST Act)
Section 9(1) / 5(1): Regular Levy
- Applicable on all supplies except liquor for human consumption
- Taxable on transaction value under Section 15
- Max rates:
- CGST: 20%
- IGST: 40%
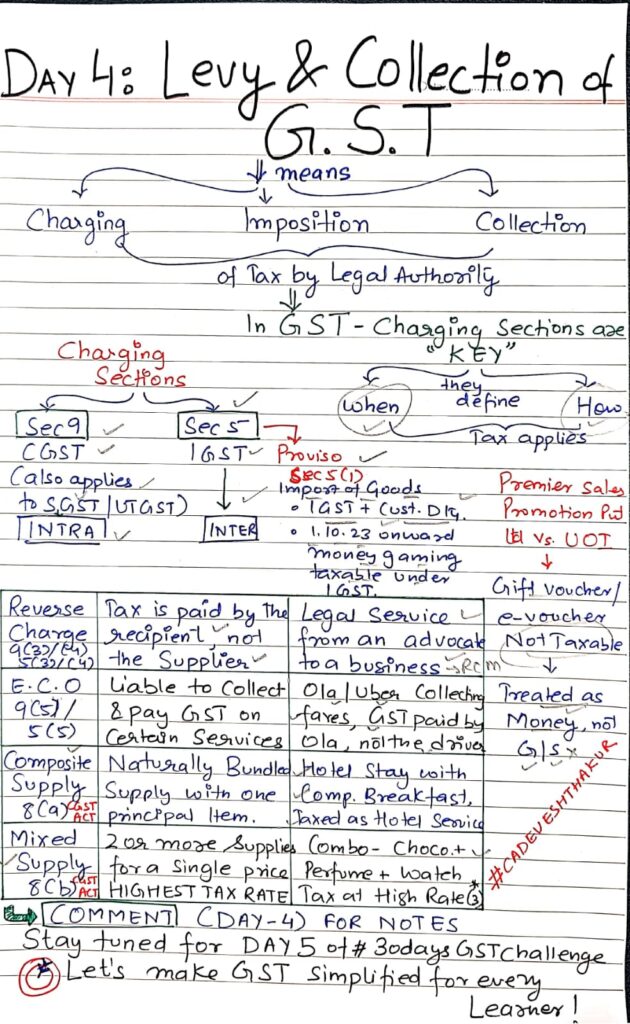
Section 9(3) / 5(3): Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM)
- Government notifies categories of supplies for which the recipient pays tax
- Ensures tax is collected even when suppliers are unregistered or difficult to monitor
Section 9(4) / 5(4): RCM for Unregistered Suppliers
- Till Oct 2017: RCM applied to unregistered to registered transactions (₹5,000 exemption limit)
- Oct 2017 – Jan 2019: RCM suspended
- Post-Feb 2019: Government can specify classes of registered persons liable to pay RCM for specific goods/services from unregistered suppliers
Section 9(5) / 5(5): E-Commerce Operators (ECOs)
- For specified services, the ECO (like Zomato, Ola) is liable to pay tax
- If no physical presence, tax to be paid by their representative in India
Judicial Insight
Premier Sales Promotion Pvt Ltd v. Union of India (2023)
Held that vouchers are not subject to GST, as they fall under the definition of money, which is excluded from GST’s scope.
Tax Liability on Composite vs. Mixed Supplies (Section 8)
Composite Supply – Treated as Principal Supply
- Naturally bundled
- Sold as a package
- Taxed at the rate applicable to principal item
Example: Hotel stay + breakfast
Mixed Supply – Taxed at Highest Rate
- Not naturally bundled
- Multiple unrelated items sold together
- Taxed at the highest applicable rate
Example: Combo of chocolates + soft drink + pen
Composition Levy (Section 10) – Simplified Taxation for Small Taxpayers
Eligibility
- Turnover limit:
- ₹50 Lakh initially
- Increased to ₹1.5 Crore for most states
Applicable Rates
| Type of Supplier | Effective Rate |
| Manufacturers (excl. notified goods) | 1% or 2% |
| Restaurant services | 5% |
| Traders (others) | 1% |
| Service Providers (under 10(2A)) | 6% |
Notified Goods Not Allowed under Composition:
- Ice Cream
- Pan Masala
- Tobacco
- Aerated Waters
- Bricks and Tiles (from Apr 2022)
Service Component in Composition
- Allowed to supply services (other than restaurant/mandap/catering) up to:
- 10% of turnover or ₹5 Lakhs, whichever is higher
Exemptions in Turnover Calculation
- Interest from deposits, loans, and advances excluded from turnover for service limit
Levy on Imports – Proviso to Section 5(1), IGST Act
Pre-October 2023
- IGST levied under Customs Tariff Act
- Based on value determined for customs purposes
Post-October 2023
- For non-notified goods, same rule as before
- For notified goods (e.g. online gaming from non-taxable territory):
- IGST levied under IGST Act
- Not treated as customs duty
Future Levy on Petroleum Products
Section 9(2)/5(2) empowers Government to notify levy on:
- Petroleum Crude
- High-Speed Diesel
- Motor Spirit
- Natural Gas
- Aviation Turbine Fuel
Levy to be applicable from the date notified by the Government.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the charging sections of GST to determine applicability.
- RCM plays a critical role in ensuring compliance from unregistered or hard-to-monitor suppliers.
- Composite and mixed supply rules prevent tax manipulation and ensure clarity.
- Composition levy is a boon for small businesses to simplify compliance.
- New IGST rules for imports reflect the evolving landscape, especially in digital services.
- Petroleum products still await full inclusion under GST – a critical reform to watch!
Stay tuned for Day 5, where we’ll explore the concepts of Time of Supply under GST — when exactly GST becomes payable!
If you found today’s blog helpful, share it with fellow learners and join the mission to make GST easier for everyone.
📌 #GSTChallengeWithDevesh | #Day4 | #GSTBasics | #CompositionScheme | #ReverseCharge | #EcommerceGST | #IGST | #GSTLaw | #TaxSimplified