Author: CA Devesh Thakur
Category: GST Basics | 30 Days GST Challenge – Day 5
Introduction
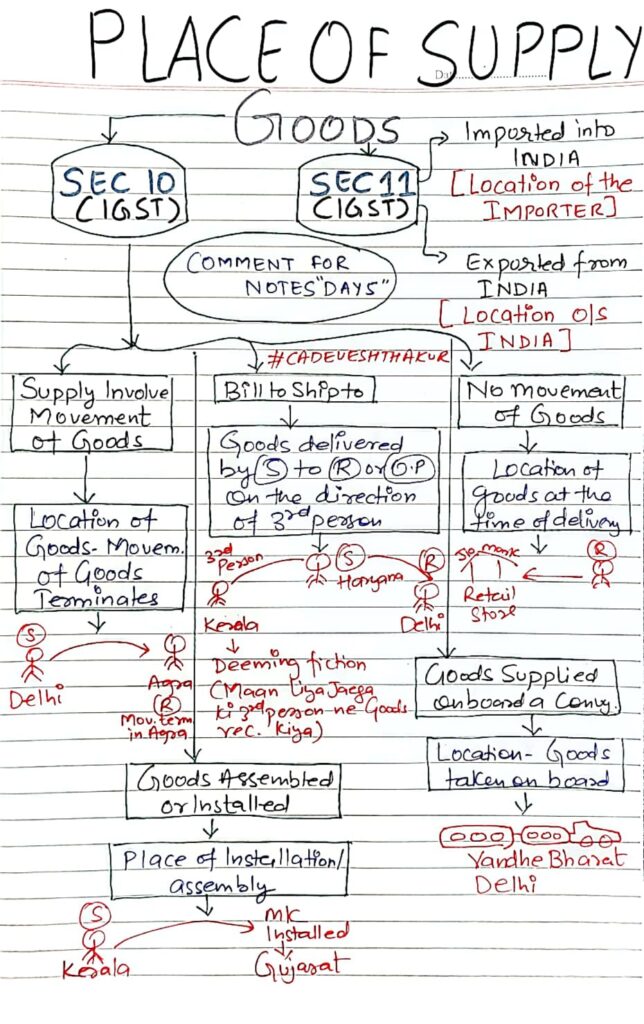
The concept of Place of Supply plays a crucial role in determining whether a supply is inter-state or intra-state, which further affects whether IGST or CGST & SGST will be levied. For goods, this is governed by Sections 10 and 11 of the IGST Act.
Let’s decode these sections with practical illustrations.
Applicable Provisions: Sec 10 & Sec 11 of IGST Act
Section 10 – When the supply of goods is within India
This section applies when both supplier and recipient are located in India.
Section 11 – When the supply of goods involves import/export
This section deals with supplies where either the supplier or recipient is located outside India.
Section 10 – Detailed Scenarios and Examples
Movement of Goods by Supplier, Recipient or Other Person
Provision:
If the supply involves movement of goods (by the supplier, recipient, or any other person), the place of supply is the location where movement terminates for delivery.
Example:
- Supplier (S) in Delhi sends goods to recipient (R) in Agra.
- Movement terminates in Agra.
Place of Supply: Agra (Uttar Pradesh)
Inter-State Supply – IGST Applicable
“Bill To – Ship To” Scenario
Provision:
When goods are delivered by the supplier to a third person on the direction of the buyer (deemed recipient), the place of supply is the location of the person who gave the direction.
Example:
- Buyer (3rd Person) in Kerala instructs Seller (S) in Haryana to deliver goods directly to another recipient (R) in Delhi.
- Though goods are delivered to Delhi, they are billed to Kerala.
Place of Supply: Kerala
Deemed that 3rd person has received the goods
No Movement of Goods
Provision:
When there is no movement of goods, the place of supply is the location of the goods at the time of delivery.
Example:
- Goods picked up by buyer from a retail store in Delhi.
Place of Supply: Delhi
Intra-State Supply – CGST + SGST Applicable
Goods Installed or Assembled at Site
Provision:
If goods are supplied and are to be installed or assembled at a site, the place of supply is the place of installation/assembly.
Example:
- Machinery sent from Kerala and installed in Gujarat.
Place of Supply: Gujarat
Tax determined based on location of installation
Goods Supplied on Board a Conveyance
Provision:
Where goods are supplied on board a conveyance (e.g. train, aircraft, vessel), the place of supply is the location at which such goods are taken on board.
Example:
- Goods supplied on Vande Bharat train while boarding in Delhi.
Place of Supply: Delhi
Section 11 – Import and Export of Goods
Goods Imported into India
Provision:
Place of supply for imports is the location of the importer.
Example:
- Goods imported by a company in Mumbai.
Place of Supply: Mumbai
Goods Exported from India
Provision:
Place of supply for exports is outside India, but for GST compliance, it is deemed to be the location outside India.
Example:
- Goods exported from Delhi to the USA.
Place of Supply: USA (outside India)
Export – Zero-Rated Supply
Summary
| Scenario | Section | Place of Supply | Example |
| Movement of goods | Sec 10 | Place where movement terminates | Delhi → Agra → Agra |
| Bill to – Ship to | Sec 10 | Location of the person who ordered | Kerala orders, ship to Delhi → Kerala |
| No movement of goods | Sec 10 | Location at time of delivery | Picked from Delhi retail store → Delhi |
| Goods installed/assembled | Sec 10 | Place of installation/assembly | Installed in Gujarat → Gujarat |
| Supplied on a conveyance | Sec 10 | Location where goods taken on board | Vande Bharat, boarded in Delhi → Delhi |
| Import of goods | Sec 11 | Location of importer | Importer in Mumbai → Mumbai |
| Export of goods | Sec 11 | Outside India | Export to USA → Outside India |
Conclusion
Understanding the Place of Supply is key to determining the correct GST liability. Whether you’re a trader, manufacturer, or a service provider dealing in goods, a correct classification under Section 10 or 11 of the IGST Act can ensure compliance and smooth business operations.




